What is Wi-Fi Calling and How Does it Affect You?
The underlying technology to support Wi-Fi calling has been available for many years. However, it is only recently that telecom companies have started rolling it out on their networks. So what is Wi-Fi calling, and why should you care about it? That’s what we will discuss in this article and show you how to enable Wi-Fi calling on your iPhone or Android device. Without any further delay, let’s get started.
What is Wi-Fi Calling?
As the name tells, Wi-Fi calling is a feature that enables users to make phone calls using Wi-Fi instead of a cellular connection. It relies on IP networks to connect phone calls over the internet instead of the cell tower. That could mean using a Wi-Fi connection at home or any other Wi-Fi hotspot accessible when you are out and about, such as at a cafe or library. Also known as Voice over Wi-Fi (VoWIFi), the protocol enables users to make and receive voice calls even without cellular reception. As long as there’s a Wi-Fi hotspot that the phone can latch on to, you can make calls to a mobile phone or a landline number. Another requirement for Wi-Fi calling is a VoLTE-enabled device, which has become commonplace since the advent of 4G several years ago.
As a user, Wi-Fi calling is almost identical to making a regular phone call without using a third-party app. The authentication, call connection, call routing all work as a regular call, as the technology is essentially the same as VoLTE. However, instead of using the carrier’s cellular network to place the call, VoWiFi uses a local Wi-Fi hotspot for the task. While VoWiFi is somewhat similar to VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) in some aspects, they differ in some critical areas insofar as their implementations are concerned. It is also different from VoWLAN, which is essentially VoIP over a Wi-Fi network.
How Does Wi-Fi Calling Work?
Wi-Fi calling is based on a protocol called GAN, or Generic Access Network. It extends mobile voice and data applications over Internet Protocol networks to enable communication over the internet, bypassing cellular networks altogether. Essentially, GAN allows cellular communication packets to be forwarded to a network access point over the internet, rather than over-the-air using cellular networks. Unlike VoIP calls, VoWiFi is only possible if both your carrier and your phone support the feature. That is different from how typical VoIP apps work. The VoIP apps do not need any additional support from either the carrier or the device. As long as a VoIP app is available for your platform, you can make VoIP calls to everyone using the same app. That is why you can call just about anybody with a smartphone using apps like WhatsApp, Google Duo, or Skype.
Difference Between Wi-Fi Calling and VoIP
VoIP transfers voice data packets over the Internet without ever routing the communication through the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or the standard telephone service. As for VoWiFi, it reaches your carrier over the Internet instead of a cell tower to establish a phone line over the PSTN. From the user’s point of view, the biggest difference between Wi-Fi calling and VoIP services is that the former lets you place and receive calls using your phone number, while a third-party VoIP service requires you to sign up separately. From a technology standpoint, VoWiFi gives carriers more control, unlike VoIP services such as Skype, WhatsApp, or Google Duo.
Advantages of Wi-Fi Calling
Works in Spotty Network Locations
The biggest advantage of Wi-Fi calling is that it will keep you in touch with your loved ones irrespective of how bad the nearby cell signal is. It is available on most major mobile networks around the globe, enabling users to place regular phone calls by connecting to a Wi-Fi network rather than a cell phone tower. It even improves voice quality in areas that have weak network coverage.
Extends Battery Life
Another advantage of this feature is that it can extend the battery life of your phone. Continuously searching for a cellular network can drain your phone’s battery quickly, especially in some areas with poor or patchy reception. Meanwhile, Wi-Fi calling is more battery efficient. It connects to one Wi-Fi network and remains available until you disconnect. It does not have to constantly search for networks, thereby improving battery efficiency.
No Additional Charges
Another benefit of Wi-Fi calling is that it typically incurs no additional charges. While the exact details differ based on the company policy and government regulations, Wi-Fi calls on US networks are generally included in the monthly voice plan. However, while it requires no add-on services or special plans, calls may count toward your minutes unless you have an unlimited voice plan.
No Third-party App Required
Finally, VoWiFi doesn’t need a separate application because it uses your regular phone number. That means you do not have to download a third-party app to make phone calls. The service also doesn’t require high bandwidth, typically consuming around ~1MB of data per minute of voice calls and ~5-10MB of data per minute of video calls. The exact amount of data consumption, however, depends on the audio and video quality (resolution such as 720p vs 1080p vs 4K, bitrate, etc.) of your Wi-Fi calls.
Disadvantages of Wi-Fi Calling
There are, however, a few negatives of Wi-Fi calling when compared to traditional mobile calls. Using the internet to route phone calls means VoWiFi suffers from the same disruptions and latency issues as VoIP calls. It is especially true for slower internet connections, which may cause the voice quality to suffer if many people are using the same Wi-Fi hotspot. It usually happens in crowded places like airports or stadiums. Faulty network connections may also lead to echoes or delays while making Wi-Fi calls. The lag is especially noticeable while making video calls using VoWiFi. That is why it is best to stick to traditional calls if you are in an area with proper cellular reception. While this feature doesn’t incur additional charges, many carriers count such calls towards their users’ allocated minutes. On top of that, it consumes Wi-Fi data, although the actual usage is relatively on the lower side.
Hardware and Software Requirements
As you already know by now, Wi-Fi calling doesn’t need a third-party app. However, it does require support from both the device manufacturer and your carrier. The feature is available on most global telecom networks. You can technically activate it on most LTE devices with a software update, but there has to be baseband support as well. Most of the major smartphone vendors have also rolled out updates over the past few years to enable the feature on their devices. Samsung, Nokia, Xiaomi, Realme, OnePlus, and Oppo have rolled out Wi-Fi calling support on many of their smartphones. You can check out some of the devices that support Wi-Fi calling in India. Do note that it is not a comprehensive list because almost all new smartphones support the feature.
Carrier Support in the US, India, and Around the World
In the US, all four major US carriers, including Verizon, AT&T, T-Mobile, and Sprint, provide built-in Wi-Fi calling support. Republic Wireless and Google Project Fi also offer VoWiFi on select devices. Republic Wireless gets support from Sprint’s network if the connection is unavailable, while Google uses T-Mobile, Sprint, and US Cellular. In India, the DoT (Department of Telecommunications) approved the proposal for public Wi-Fi calling back in 2018. Following that decision, leading telecom service providers in the country, including Jio, Airtel, and Vi (formerly Vodafone-Idea), have rolled out the service on their respective networks.
Here are some of the leading telecom operators across the world that offer Wi-Fi calling on their networks:
USA: At&T, Verizon, T-Mobile, Sprint, Metro PCS, Ting, C Spire, Simple Mobile, GCI, Appalachian Wireless India: Jio, Airtel, Vi (pronounced ‘we’) Austria: A1 Belgium: Telenet Czech Republic: T-Mobile, Vodafone Denmark: 3, TDC, Telenor France: Orange, Bouygues Germany: O2, Telekom, Vodafone Greece: Cosmote Ireland: Eir Liechtenstein: Swisscom Netherlands: Vodafone Norway: Telia, Telenor Poland: Orange, Play, T-Mobile Romania: Orange Spain: Orange Sweden: 3 Switzerland: Salt, Swisscom, Sunrise Turkey: Turkcell, Vodafone United Kingdom: 3, O2, Vodafone, EE Australia: Optus, Telstra Hong Kong: 3, SmarTone, 1O1O and CSL, China Mobile Hong Kong Malaysia: Digi, U Mobile Singapore: Singtel Taiwan: APT, FarEasTone Thailand: AIS, True Move, dtac Argentina: Claro Brazil: Claro, Vivo Panama: +Móvil Puerto Rico: AT&T, T-Mobile USA, Sprint Wireless U.S. Virgin Islands: AT&T, Sprint Wireless South Africa: CellC, Vodacom Israel: Partner Saudi Arabia: Zain United Arab Emirates: Etisalat
Note: This is not really a comprehensive list, but should still offer an indication of how ubiquitous the technology has become over the past few years.
How to Enable Wi-Fi Calling on iPhone and Android
Most of the major carriers in the US, Europe, and India offer Wi-Fi calling without any additional charges. You can activate the feature on your iPhone by going to Settings -> Phone app -> Wi-Fi Calling -> Wi-Fi Calling on This iPhone. Toggle on the button next to it and enjoy voice calling over the Internet.
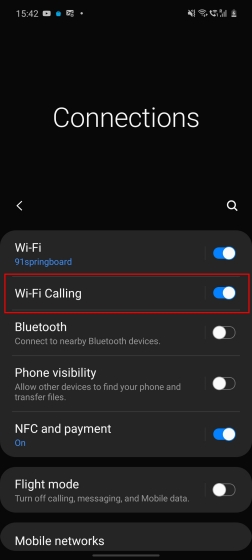
For Android devices, the exact method to enable the feature differs from one smartphone to another. For example, on Samsung devices running OneUI, go to Settings -> Connections -> Wi-Fi Calling -> SIM1 or SIM2 -> toggle on Wi-Fi Calling. On OnePlus devices, open Settings -> WiFi and Internet -> SIM and network settings -> SIM to enable VoWiFi. Wi-Fi calling is also available on a host of Nokia, Xiaomi, and Realme smartphones. To learn more, check out how you can enable Wi-Fi calling on any iPhone or Android device.
VoWiFi: Stay Connected in Areas With Spotty Cellular Coverage
Wi-Fi calling or VoWiFi is a highly useful feature that lets you stay connected to your loved ones even in areas with weak cellular coverage. Now that you know more about it, check out some of our other detailed explainers on the latest Wi-Fi and cellular standards, including 5G networks and Wi-Fi 6E. Also, check out the best VoIP apps on Android and iOS, which should come in handy if your phone or carrier does not support Wi-Fi calling. Finally, check out the best call recorder apps on Android and on iPhone.